Introduction
Chatbot is one of the promising technologies in supporting the digital transformation efforts of many organizations in both public and commercial sector. It is being used to complement human-assisted customer service to improve end user experience of consumers and citizens. They enable highly conversational user interaction with software applications through voice and text, on multiple delivery platforms. They are finding use in almost all sectors of the industry – retail, financial, healthcare, state and local citizen service etc. Together with the increasing use of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) the digital transformation is moving to the next level.
This white paper will provide a general overview of the chatbots and how they work, current and predicted applications, and some of the tools available for implementation.
Overview of Chatbots
A Chatbot can be defined as a computer program designed to simulate conversation with human users. Chatbots were created to mimic human conversation, so companies could communicate with customers in an easier way reducing dependency on human workers and move customers towards more and more self-service. These can be thought of as an extension of chat features that many of the web sites provide but without a human at the backend answering interacting with the customers. Chatbots are commonly used for verbal and nonverbal interactions with a user through online browsers, messaging services, apps, voice commands, etc. It leverages multiple technologies such as Natural Language Processing (NLP), Speech Recognition and Machine learning to artificially replicate human interactions and provide answers based on previous interactions. As the Chatbot is in use it will progressively learn more about the audience and work with more accuracy and precision. NLP is a key part of how the Chatbot works so well. The Chatbot itself communicates with the NLP layer which in turn works with the Knowledge Base and Data Storage to communicate back and forth with the user. The NLP process itself is comprised of 5 steps: tokenization, sentiment analysis, normalization, named entity recognition, and dependency parsing. Tokenization separates phrases into linguistically separate tokens. Sentiment analysis studies the user’s experience and will transfer them to a human when needed. Normalization processes the text to root out typing or spelling errors that might alter the meaning. Named entity recognition looks for categories of words similar to the information the user requires, and Dependency Parsing looks for similar verbs, objects, phrases, and nouns than in the text to determine what the user wanted to convey.
Chatbots and Cloud
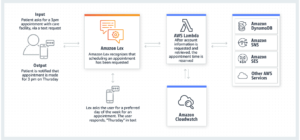
Cloud computing is playing a major role in increasing the popularity of Chatbots as much of the computing capabilities needed to implement Chatbots are available via the cloud service providers. For example, Amazon Lex is a service on AWS, that provides advanced deep learning functionalities of automatic speech recognition (ASR) for converting speech to text, and natural language understanding (NLU) to recognize the intent of the text and build highly conversational interfaces for interacting with enterprise applications, customer support etc., for both internal and external users of an organization’s services. These are the same technologies that power Amazon Alexa. The following diagram illustrates the various AWS services involved in developing a chatbot that helps a patient schedule their own appointment with their healthcare provider.
(Source: AWS)
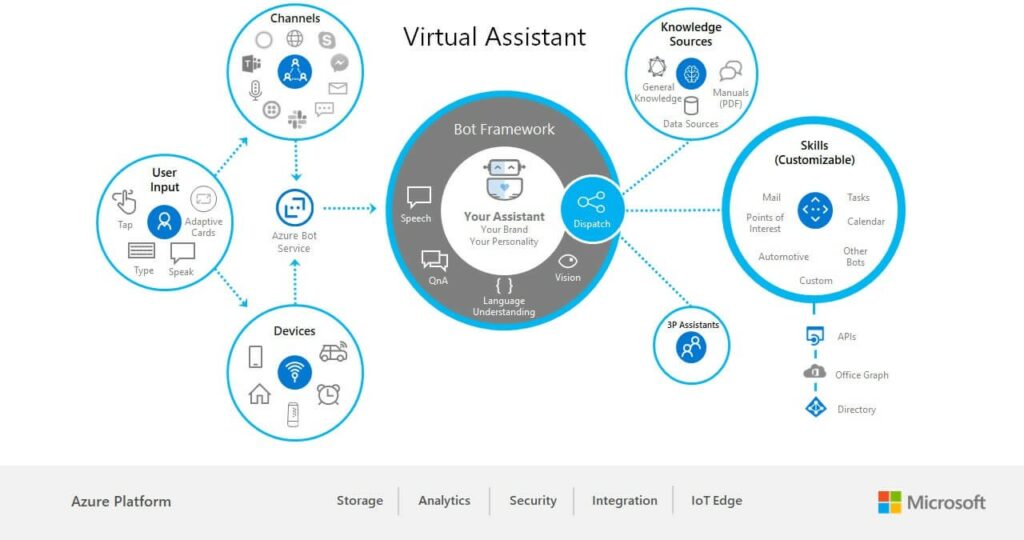
Similar to the framework provided by AWS, Microsoft Azure provides Azure Bot Service, a purpose-built managed service for developing bots. The service can be integrated across multiple communication channels such as website, apps, Microsoft Teams, Skype, Slack, Cortana and Facebook Messenger to reach a wide variety of audience. The diagram below illustrates the Azure Bot framework.
(Source: Microsoft)
Current State of Chatbots
Companies have been using Chatbots effectively for a variety of applications such as entertainment, personal assistance, shopping, outreach, customer service, IT, and healthcare. Chatbots have the potential to be an even more influential feat than they already are if businesses continue to pursue them and apply them to a variety of fields. We continue to see increased adoption of this technology and integration with other emerging technologies such as RPA. One of the areas that has a tremendous potential for this is the healthcare domain – Patients, providers and insurance companies. Some example applications include mental health assistants, appointment management, insurance navigators, care search, etc.
With the introduction any new technology that attempts to replace human interactions there are both positive and negative impacts. Chatbots is one such technology that falls into that category. The programmability of the Chatbot makes it easy to adapt to the targeted audience but at the same time too much personalization can cause some unintended issues. The Drift’s 2018 State of Chatbots Report[1] showed potential benefits of Chatbots for millennials and baby boomers and concluded that both generations believe Chatbots are most beneficial for their 24-hour service, getting an instant response, and answers to simple questions . While Chatbots do have many strengths and the potential to be impactful in society, there are still issues that companies need to fix now so consumers trust the technology. In May of 2018, a survey of user ages 18+ by Helpshift[2] reported that 50.7% find that Chatbots keep them from a live person, 47.5% say that there are too many unhelpful answers, and 39.5% say that in the end, they redirect them to self-serve FAQs. The two biggest problems were misunderstanding requests and misunderstanding the nuances of human dialogue. These are all things the companies have acknowledged and are actively trying to improve their algorithms to address these concerns.
Why Unissant?
At Unissant’s Innovation Center, we have experimented with various chatbot platforms, including cloud-based solutions. We have found that existing out of the box solutions and frameworks are generic and are not fit for most of the customers’ requirements. Unissant’s internal R&D capabilities, in addition to collaboration with companies who are leaders in natural language processing, understanding and generation position us well to support our customers in their digital transformation journey. We work with our customers to develop domain specific Chatbots using our own hybrid agile approach.
References